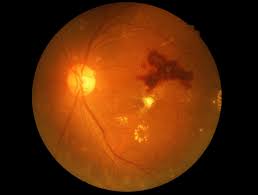
Important points to know about diabetic retinopathy
Diabetic Retinopathy is an eye problem which occurs when the blood vessels in the eye gets damaged. This disease is common in people who don’t properly manage their diabetes or have been diabetic for a long time.
Many people fail to notice the symptoms in the beginning, which makes the disorder grow and become more severe. DR should be taken seriously because if left untreated, it can result in complete eye blindness and vision loss.
DR can be classified into two simple types:
● Non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR): This is the mild stage of DR. A person with NPDR may not notice any symptoms
● Proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR): Also called the advanced diabetic retinopathy, PDR is the serious stage when the eye develops abnormal blood vessels
33% of diabetic patients (285 million people estimated) show some signs of this disease, worldwide.
In a nutshell
● Diabetic retinopathy is a complication common in Diabetic patients
● The eye disorder is triggered by damaged blood vessels in the retina
● It can lead to blindness in severe cases
● Some signs of DR are colour blindness and floaters in the vision
● For prevention, diabetic patients should get their vision checked every year
● Retinal surgery is used to treat DR. Diabetic patients can prevent it from happening by keeping the blood sugar levels in check
Symptoms
You may not be able to notice any symptoms if the eye disorder is in its early stages. However, as the problem becomes severe, you may start to experience some signs.
● Blurred or impaired vision
● Difficulty in accurately recognizing colours
● Struggling with night vision
● Having spots at the centre of your vision
Women who have diabetes and are going through their menstrual period are at a bigger risk of Diabetic Retinopathy. If you notice any signs like change in your vision or blurriness, take the assistance of an eye specialist.
Diagnosis
As discussed earlier, the early symptoms of DR are not easy to catch. If you are a diabetic patient, it is recommended that you get your eyes checked annually or twice a year to avoid any eye disorder that occurs as a diabetic complication.The diagnosis of DR involves a comprehensive eye examination. Retina and macula are carefully inspected.
An eye specialist will take the following steps to diagnose RD:
● Examine your history of diabetes and other diseases which affects the eyes
● Measure the visual loss that has occurred
● Refraction to find out whether you need a new prescription
● Inspection of the retina through pupil dilation
● Measurement of pressure present in the eye
Tests that may help the doctor diagnose the disorder:
● Dilated Eye Exam
● Fluorescein angiography
● Optical coherence tomography (OCT)
Treatment
Both Advanced Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR) and NPDR can be treated. Your eye doctors will suggest the most suitable method after completely studying your case. However, the following treatments are most commonly used to get rid of diabetic retinopathy in the eye.
● Vitrectomy
● Focal laser treatment, or photocoagulation
● Scatter laser treatment, or pan-retinal photocoagulation
How to prevent Diabetic Retinopathy?
You can prevent DR by properly managing your blood sugar levels. Whether it’s taking the right diet or exercising every day, a healthy lifestyle will keep you away from numerous diabetic complications including DR.
Who is at the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy?
● People with extensive diabetes history
● Someone who does not manage his diabetes carefully
● People with high blood cholesterol and blood pressure
● Women who are going through pregnancy
● People who smoke
Complications
The eye is a sensitive organ. As your blood vessels grow abnormally, it can cause you a few other complications:
Vitreous haemorrhage. When the weak blood vessels leak into the jelly-like substance which is situated in the centre of the eye, there is a risk of vitreous hemorrhage. This disease will make the vision hindrance worse and in worse cases, if the bleeding is severe, it can completely block your eye vision.
Retinal detachment: Retinal detachment is an eye disorder in which the retina is pulled away from the eye. If the blood vessel damages the tissue leaving a scar, it can detach the retina.
Glaucoma: New blood vessels are formed in the front of the eye and disturb the fluid flow out of the eye. This creates pressure on the eye that can harm the optic nerve — a nerve that conveys image signals from the eye to the brain.